28++ Equation For Velocity Pressure
Equation For Velocity Pressure. Δp major_loss = λ (l / d h) (ρ f v 2 / 2) (1). The thrust is then equal to the exit mass flow rate times the exit velocity minus the free stream mass flow rate times the free stream velocity.

Bernoulli’s equation can be considered a statement of the conservation of energy principle appropriate for flowing fluids. Free online gas law calculator using the van der waals equation which accepts different input metric units such as temperature in celsius, fahrenheit, kelvin; P 1 = inlet pressure (n / m 2, pa) p 2 = outlet pressure (n / m 2, pa) p c.
escalier exterieur metal prix feuille de placage melamine galette des rois 2019 recette originale felicitaciones por 50 anos de casados
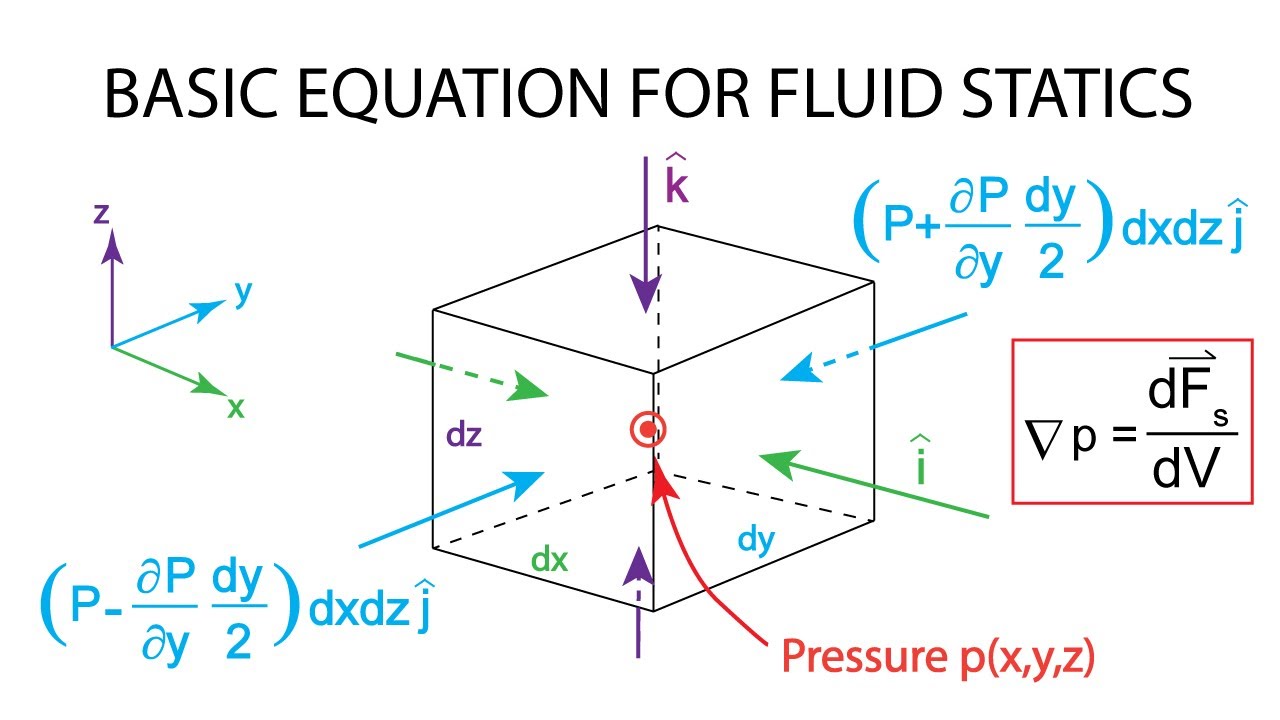
Introductory Fluid Mechanics L4 p2 Basic equation of
Δp major_loss = major (friction) pressure loss in fluid flow (pa (n/m 2), psf (lb/ft 2)). Meter per second is the s.i. A pitot tube can also give an estimate of the flowrate through a pipe or duct if the pitot tube is located where the average. The relation between pressure and velocity can be given through two independent equations/formulation.

By applying the continuity equation, the velocity of the fluid is greater in the narrow section. The bernoulli equation models the physical situation very well. Note that c 2 is independent of p 2 and that the nozzle flow is a maximum. The joukowski impulse equation is used to calculate the resulting pressure when the liquid velocity that drops to.

For our first look at the equation, consider a fluid flowing through a horizontal pipe. Bernoulli's equation has some surprising implications. When the kinetic energy is that of fluid under conditions of laminar flow through a tube, one must take into account the velocity profile to evaluate the kinetic energy. The density of the air, in turn, is a function.
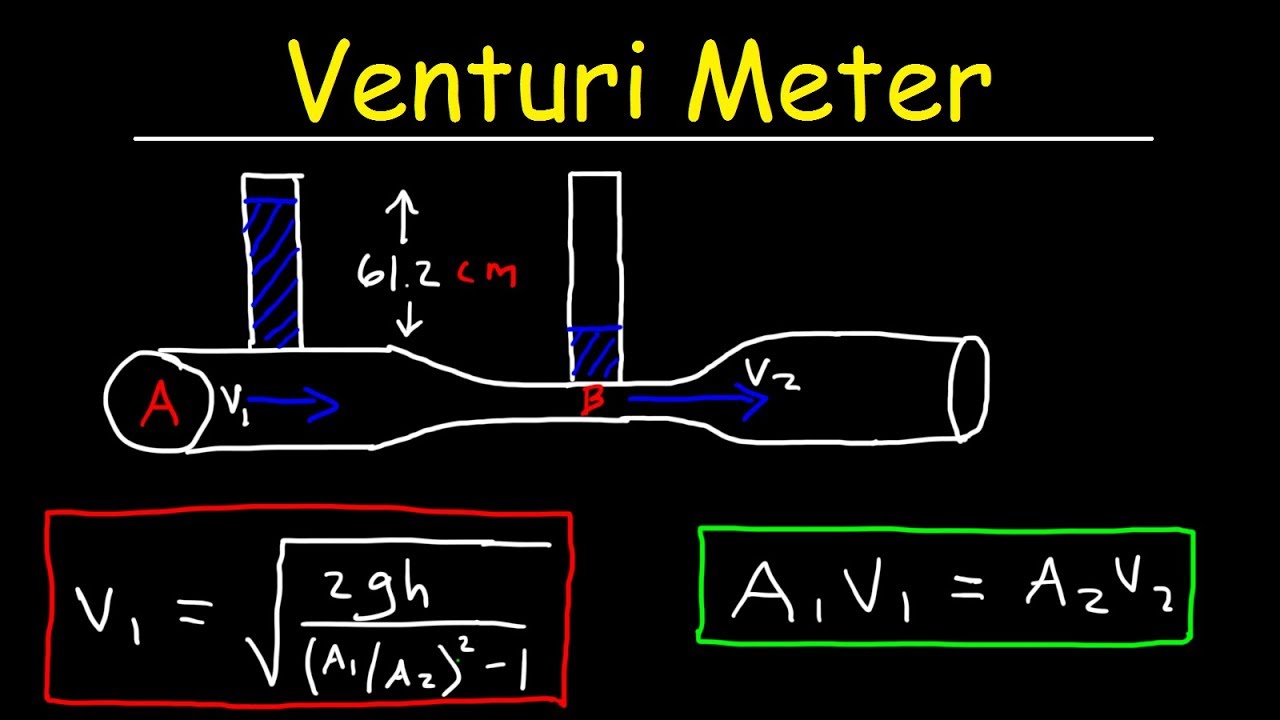
That makes it sound like a decrease in pressure is caused by an increase in velocity, when it's more that an increase in velocity is caused by a decrease in pressure. In the comparison of pressure velocity relation, one thing is common, and that is, both are macroscopic parameters that govern plenty of natural occurrences. Bernoulli’s equation states mathematically that.

R ≤ r c the following equation applies; • loss coefficients are a function of velocity pressure, pv • if the section velocity pressure is used, all loss coeffients can be added and multiplied by the sections velocity pressure to determine the dynamic losses for the section • if the common velocity pressure is used , then the individual losses.

The density of the air, in turn, is a function of the local atmospheric pressure and the temperature. In the comparison of pressure velocity relation, one thing is common, and that is, both are macroscopic parameters that govern plenty of natural occurrences. A pitot tube can also give an estimate of the flowrate through a pipe or duct if the.
R ≤ r c the following equation applies; Bernoulli’s equation can be considered a statement of the conservation of energy principle appropriate for flowing fluids. Velocity is a vector quantity as both speed and direction are required to identify it. The relationship between flow, velocity, and pressure can be explained using bernoulli’s principle. When outlet pressure p 2 equal to.

Not flowing under pressure, and was first presented in. By applying the continuity equation, the velocity of the fluid is greater in the narrow section. Volume flow rate and equation of continuity. Velocity head.thus, the three terms of velocity head, elevation head, and pressure head appear in the head equation derived from the bernoulli equation for incompressible fluids: The dynamic.