39+ Equations Of Motion Suvat
Equations Of Motion Suvat. The greatest speed of an oscillator is at the equilibrium position ie. Suvat is an acronym of the five variables that describe a system in motion with constant acceleration:

Projectile motion (part i) projectile motion (part ii) forces. Students can complete this set of questions interactively on the dfm homework platform. (no credit will be given for answers which use any of the kinematics (suvat) formulae listed under mechanics in the as mathematics section of the formulae booklet.) (4)
escalier 12 tournant avec palier elkhorn hot springs resort fraises defonceuse brico depot g4 led bulb
Projectile Motion Portfolio of Physics
Velocity is a fundamental concept in kinematics, the branch of classical mechanics that describes the motion of bodies. The speed of an object in simple harmonic motion varies as it oscillates back and forth. 60 km/h to the north). Velocity is a physical vector quantity;

60 km/h to the north). Now, let's make a choice. Can you derive the suvat equations? If s represents the displacement of the object, then: As we have already discussed earlier, motion is the state of change in position of an object over time.

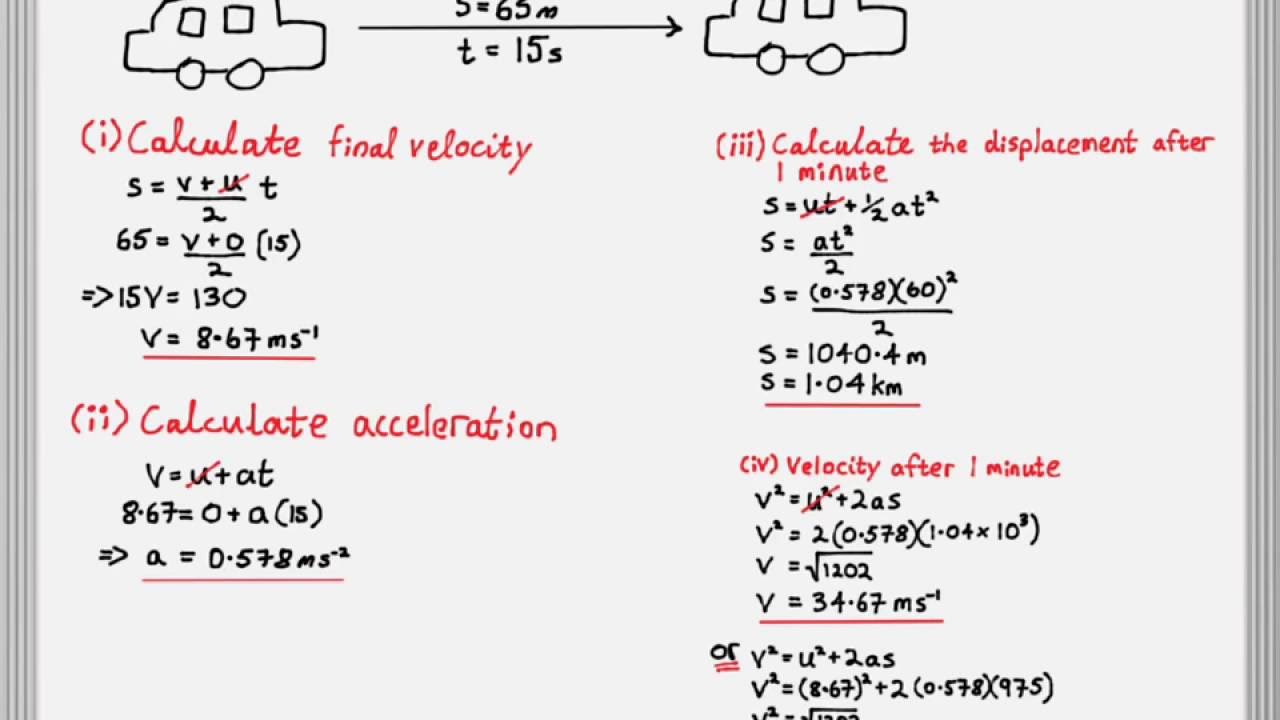
Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity of an object. Displacement s, initial velocity u, final velocity v, acceleration a, and time t. Kinematics is the science of describing the motion of objects using words, diagrams, numbers, graphs, and equations. Stopping, thinking and braking distances. So we can just write down two copies of this equation for the given.

It is described in terms of displacement, distance, velocity, acceleration, time and speed. Projectile motion (part i) projectile motion (part ii) forces. V = u + at; These equations are valid only when the acceleration is constant. Onlinecalculator.guru is the most trusted online portal that helps students offering free calculator on physics, math, and many other topics.

Exam questions for c1, c2, c3, c4, s1 and m1 arranged by module and topic. As we have already discussed earlier, motion is the state of change in position of an object over time. Looking at both the net force on an object and also cases. Displacement (s), initial velocity (u), final velocity (v), acceleration (a), and time (t). So.
How high it bounce after being dropped from a given height h where the impact had a coefficient of restitution e. It concerns only variables derived from the positions of objects and time. Suvat is an acronym of the five variables that describe a system in motion with constant acceleration: Free maths christmas resources and activities from tes maths. V.

Although the suvat equations will no longer be valid, it is still possible to find the position or the velocity from the acceleration through integration. The speed of an object in simple harmonic motion varies as it oscillates back and forth. What is the best online website that offers all physics calculators? This equation can be rearranged to give: Velocity.