13+ Equation Of Ellipse And Hyperbola
Equation Of Ellipse And Hyperbola. So let's solve for the focal length. The straight line y = mx ∓ √[a 2 m 2 + b 2] represent the tangents to the ellipse.

Intersecting straight lines) if a' and c ' have opposite signs i.e. Length of latus rectum of hyperbola. The focal length, f squared, is equal to a squared minus b squared.
ersatz lampenschirm glas e14 electrovanne arrosage hunter escalier quart tournant haut gauche pas cher equations of motion suvat
Ex Find the Equation of an Ellipse Given the Center
A hyperbola the set of points in a plane whose distances from two fixed points, called foci, has an absolute difference that is equal to a positive constant. A conic section is the locus of a point that advances in such a way that its measure from a fixed point always exhibits a constant ratio to its perpendicular distance from a fixed position, all existing in the same plane. Where f is the distance between the foci, p and q are the distances from each focus to any point in the ellipse. A hyperbola the set of points in a plane whose distances from two fixed points, called foci, has an absolute difference that is equal to a positive constant.
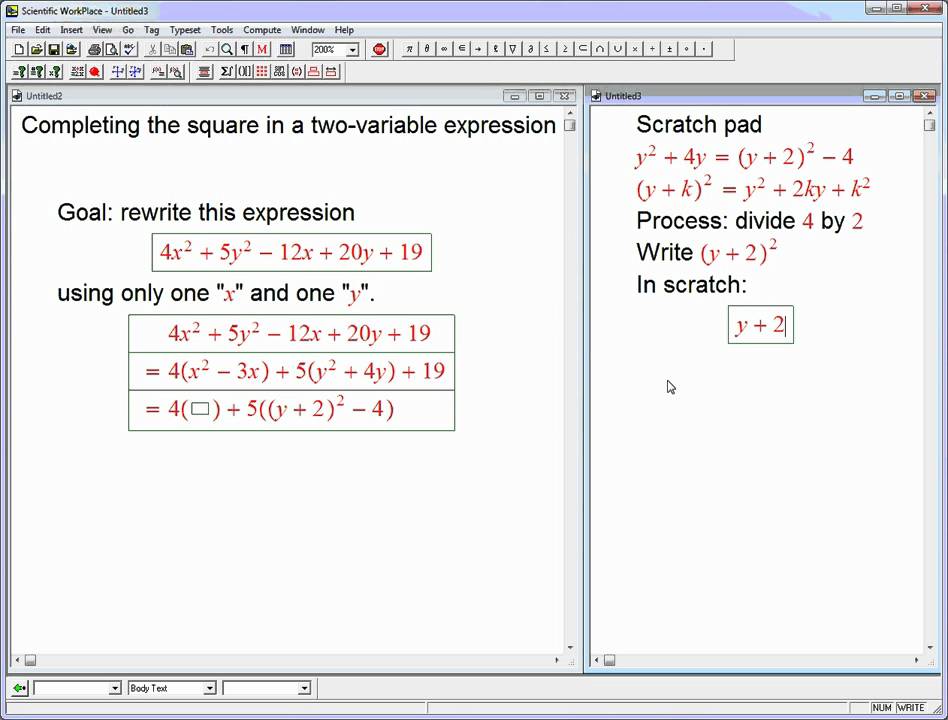
And in future videos i'll show you the foci of a hyperbola or the. A conic section is the locus of a point that advances in such a way that its measure from a fixed point always exhibits a constant ratio to its perpendicular distance from a fixed position, all existing in the same plane. Slope form of a tangent.

If the line y = mx + c touches the ellipse x 2 / a 2 + y 2 / b 2 = 1, then c 2 = a 2 m 2 + b 2. What type of conic section is the following equation? The equation of the tangent to an ellipse x 2 / a 2 + y 2.

- a hyperbola (or limiting form of hyperbola: In other words, if points f 1 and f 2 are the foci. The summary for the latus rectum of all the conic sections are given below: Intersecting straight lines) if a' and c ' have opposite signs i.e. By using this website, you agree to our cookie policy.

A conic section is the locus of a point that advances in such a way that its measure from a fixed point always exhibits a constant ratio to its perpendicular distance from a fixed position, all existing in the same plane. 1) an ellipse (or limiting form of ellipse: Every ellipse has two axes of symmetry. Intersecting straight lines) if.

In other words, if points f 1 and f 2 are the foci. Every ellipse has two axes of symmetry. Where f is the distance between the foci, p and q are the distances from each focus to any point in the ellipse. And in future videos i'll show you the foci of a hyperbola or the. Then the conic.
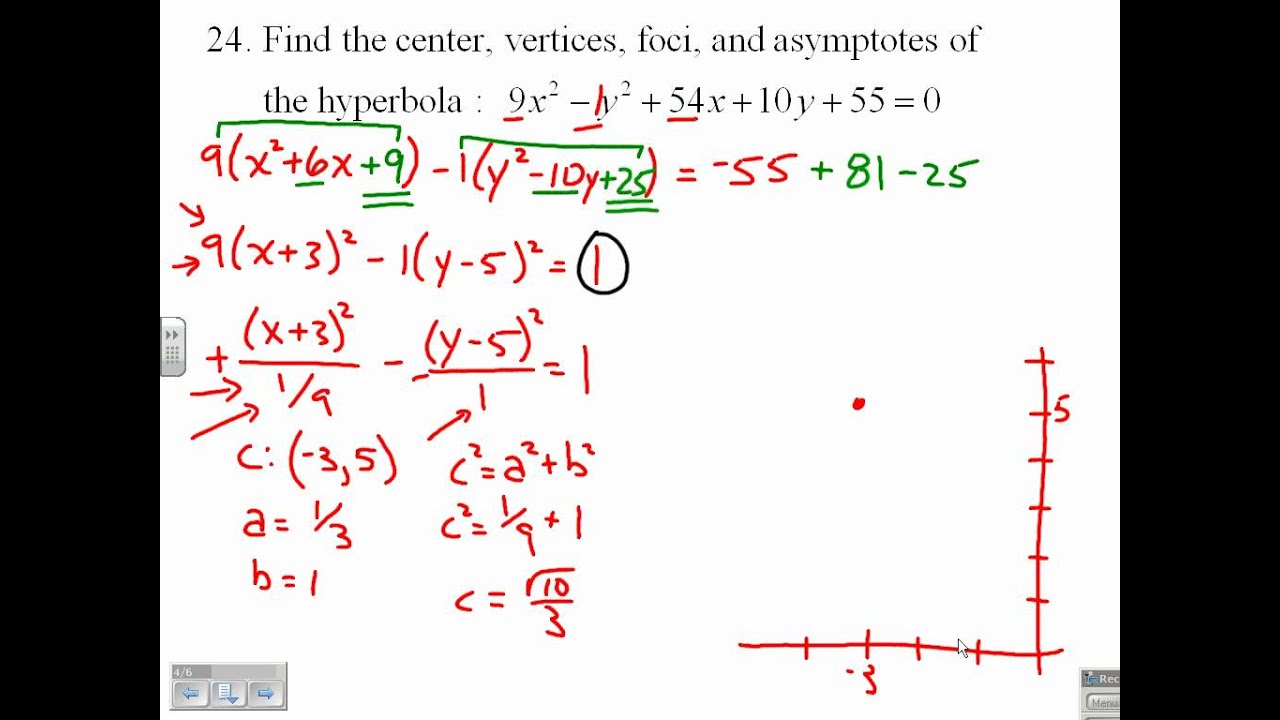
The equation of the tangent to an ellipse x 2 / a 2 + y 2 / b 2 = 1 at the point (x 1. The summary for the latus rectum of all the conic sections are given below: 1) an ellipse (or limiting form of ellipse: Then the conic represented by the equation will be. Intersecting straight lines).